Paper and cardboard with plastic lamination look like regular cardboard, but they have a thin layer of polyethylene or other plastic on their surface. This protection makes the packaging resistant to moisture and grease — which is why laminated cardboard is used for fast food boxes, gift wrapping, paper cups, confectionery packaging, and disposable containers. However, due to this plastic layer, such packaging does not belong to regular paper and is practically not recycled together with it.
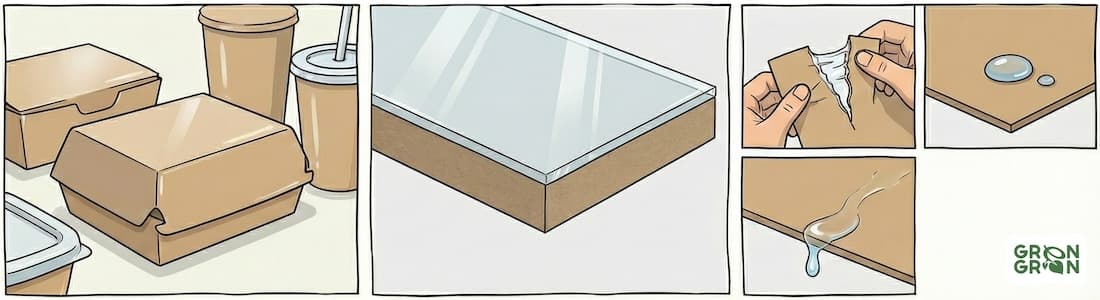
The main problem with laminated cardboard is its composite nature: paper fibers are bonded with polyethylene film, which is difficult to separate during recycling. In sorting, such packaging goes to waste because when trying to recycle it as paper, it contaminates recyclable materials with plastic.
Identifying laminated cardboard is quite simple. The most reliable signs: